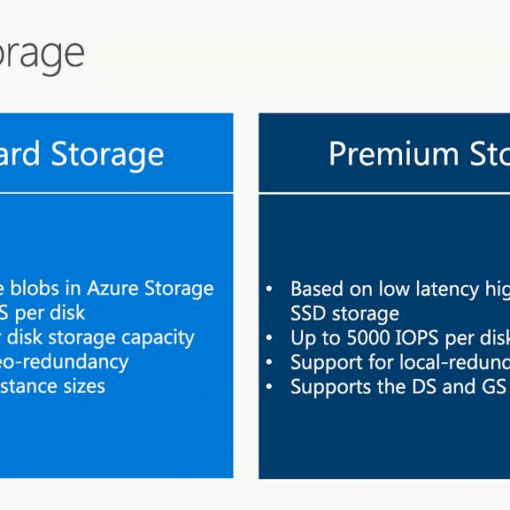
In an era where cyber threats are continually evolving, securing your cloud infrastructure has never been more critical. The Security Pillar of the Azure Well-Architected Framework provides a comprehensive approach to safeguard your applications and data. This pillar helps you design, implement, and maintain robust security controls, ensuring that your cloud environment is resilient against threats and compliant with regulatory requirements.
What is the Security Pillar?
The Security Pillar is one of the five core components of the Azure Well-Architected Framework. It focuses on protecting data, managing identities, implementing effective security controls, and establishing a strong security posture. The pillar provides guidelines and best practices to ensure that your applications and data are secure from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Importance of Security in Cloud Architecture
- Protecting Sensitive Data: Ensuring that personal and sensitive data is protected from breaches and leaks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal and regulatory requirements to avoid penalties and legal issues.
- Maintaining Trust: Building and maintaining trust with customers by ensuring their data is secure.
- Preventing Financial Loss: Avoiding the financial impact associated with data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Protecting your business operations from disruptions caused by security incidents.
Key Principles of the Security Pillar
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized users can access your applications and data.
- Least Privilege Access: Grant users the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Use RBAC to manage permissions based on user roles, simplifying access management and enhancing security.
- Threat Protection
- Advanced Threat Detection: Use Azure Security Center and Azure Sentinel to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address potential security weaknesses.
- Network Security: Implement network security groups, firewalls, and virtual networks to protect your infrastructure from external and internal threats.
- Data Protection
- Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit using Azure’s encryption services to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP policies to prevent sensitive information from being shared or accessed inappropriately.
- Secure Backup: Regularly back up your data and ensure that backups are stored securely and tested for restoration.
- Security Posture Management
- Continuous Monitoring: Use tools like Azure Monitor and Security Center to continuously monitor your environment for security threats and compliance issues.
- Compliance Management: Ensure that your environment meets industry standards and regulatory requirements by using Azure Policy and Compliance Manager.
- Incident Response: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to quickly and effectively respond to security incidents.
Implementing the Security Pillar: Best Practices
- Adopt a Zero-Trust Model Assume that threats exist both inside and outside your network. Verify every request as though it originates from an open network.
- Regular Security Training Provide ongoing security training for your team to ensure they are aware of the latest threats and best practices.
- Automate Security Tasks Use automation to enforce security policies, manage updates, and conduct regular security assessments to reduce the risk of human error.
- Use Secure Development Practices Incorporate security into your development lifecycle by following secure coding practices and conducting regular code reviews.
Use Case: Financial Services
Consider a financial services firm that handles sensitive customer information and financial transactions. By implementing the Security Pillar’s best practices, the firm can ensure that customer data is encrypted, access is tightly controlled with MFA and RBAC, and threats are continuously monitored and mitigated. This comprehensive security approach helps the firm maintain regulatory compliance, protect against cyber threats, and build trust with customers.
The Security Pillar of the Azure Well-Architected Framework is essential for building and maintaining a secure cloud environment. By following its principles and best practices, you can protect your applications and data from threats, ensure compliance with regulations, and maintain a strong security posture. Start implementing the Security Pillar today to safeguard your cloud infrastructure and ensure business continuity.