Updated – June 2024
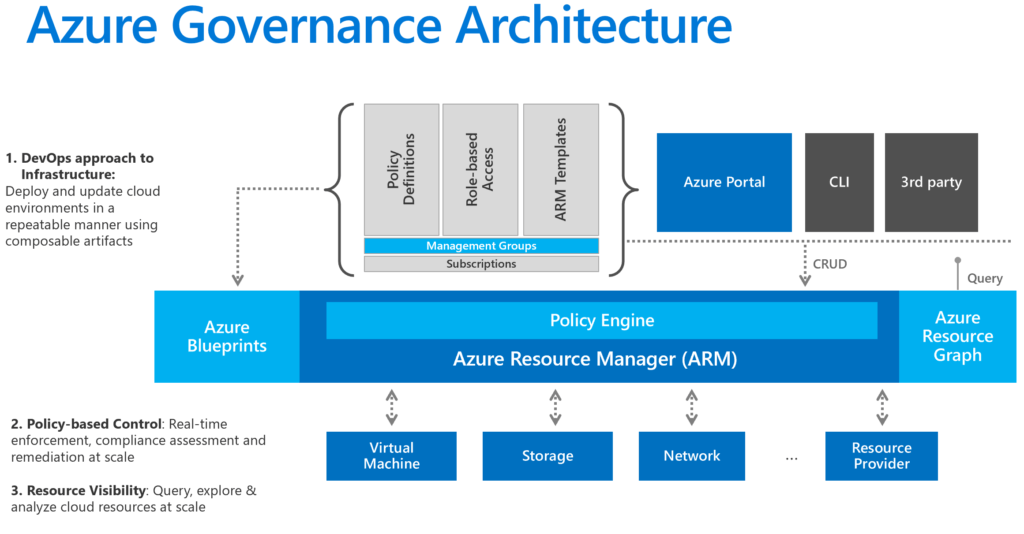
Managing a robust and secure cloud environment requires a well-defined governance strategy. Azure Governance provides a suite of tools and features to help organisations control, manage, and secure their Azure resources effectively. In this post, we’ll explore the core services and features of Azure Governance, explaining their importance and how they can be utilised to maintain a compliant and well-managed Azure environment.
What is Azure Governance?
Azure Governance refers to the set of tools and practices that ensure your Azure environment is managed efficiently, securely, and in compliance with your organisation’s policies and standards. It encompasses policy management, resource organisation, cost management, and more, enabling you to maintain control over your cloud resources.
Think of Azure Governance as the framework that keeps your cloud operations running smoothly and securely, ensuring that all resources are used responsibly and efficiently.
Some of the Core Services and Features of Azure Governance
- Azure Policy
To enforce organisational rules and ensure compliance.
Allows you to create, assign, and manage policies. For example, you can ensure that all storage accounts have encryption enabled.
Use Case: Preventing the deployment of resources in non-approved regions.
- Azure Blueprints
To provide a repeatable way to define and implement environments.
Combines templates, policies, and RBAC into a single package that can be applied to new subscriptions.
Use Case: Deploying a standardised environment for a new development project that includes specific network settings, storage configurations, and compliance controls.
- Azure Cost Management and Billing
To help organisations understand and manage their Azure spending.
Includes budgeting, cost analysis, and recommendations for cost optimisation.
Use Case: Setting budgets for different projects and receiving alerts when spending approaches the limit.
- Azure Management Groups
To organise Azure subscriptions for unified policy management.
Allows you to apply policies and RBAC across multiple subscriptions.
Use Case: Implementing a global policy that restricts resource creation to specific regions across all company subscriptions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
To manage who has access to Azure resources and what actions they can perform.
Provides fine-grained access management by assigning roles to users, groups, and applications.
Use Case: Granting a developer access to a specific virtual machine while restricting access to the production environment.
- Azure Resource Graph
To explore and query resources across multiple subscriptions.
Offers powerful querying capabilities to gain insights into your resource configurations and statuses.
Use Case: Identifying all resources that do not comply with a specific policy across all subscriptions.
- Azure Monitor
To collect and analyse telemetry data from Azure and on-premises environments.
Includes capabilities like metrics collection, log analytics, and alerting.
Use Case: Monitoring the performance of applications and receiving alerts when predefined thresholds are exceeded.
Azure Governance provides a comprehensive set of tools and features to help organisations manage their Azure environments effectively. By implementing Azure Policy, Blueprints, Cost Management, Management Groups, RBAC, Resource Graph, and Monitor, you can maintain control, ensure compliance, and optimise your cloud resources.
Sources: